RUBY
리스트를 이용한 프로그래밍(파이썬) 본문
리스트를 이용한 프로그래밍(파이썬)
1부터 사용자가 입력한 숫자까지의 약수와 소수를 리스트에 각각 저장하고, 이것을 출력하는 프로그램을 만들어보자
inputNum = int(input('1보다 큰 정수 입력: '))
listA = []
listB = []
for n in range(1, inputNum+1):
if n == 1:
listA.append(n)
else:
if inputNum % n == 0:
listA.append(n)
for number in range(2, inputNum+1):
flag = True
for n in range(2, number):
if number % n == 0:
flag = False
break
if flag:
listB.append(number)
print(f'{inputNum}의 약수: {listA}')
print(f'{inputNum}까지의 소수: {listB}')1보다 큰 정수 입력: 50
50의 약수: [1, 2, 5, 10, 25, 50]
50까지의 소수: [2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47]
1부터 100사이에 난수 10개를 생성한 후 짝수와 홀수를 구분해서 리스트에 저장하고 각각의 개수를 출력하는 프로그램을 만들어보자
import random
randomList = random.sample(range(1, 101), 10)
evens = []
odds = []
for n in randomList:
if n % 2 == 0:
evens.append(n)
else:
odds.append(n)
print(f'짝수: {evens}, 개수: {len(evens)}개')
print(f'홀수: {odds}, 개수: {len(odds)}개')짝수: [54, 86, 62], 개수: 3개
홀수: [59, 97, 21, 11, 35, 19, 57], 개수: 7개
다음은 공원 입장료를 나타낸 표이다. 1일 총 입장객이 100명이라고 할 때, 1일 전체 입장 요금을 구하는 프로그램을 만들어보자. 단, 입장 고객의 나이는 난수를 이용한다
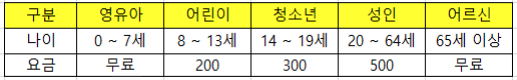
import random
visitors = []
for n in range(100):
visitors.append(random.randint(1, 100))
group1, group2, group3, group4, group5 = 0,0,0,0,0
for age in visitors:
if age >= 0 and age <= 7:
group1 += 1
elif age >= 8 and age <= 13:
group2 += 1
elif age >= 14 and age <= 19:
group3 += 1
elif age >= 20 and age <= 64:
group4 += 1
else:
group5 += 1
group1Price = group1 * 0
group2Price = group2 * 200
group3Price = group3 * 300
group4Price = group4 * 500
group5Price = group5 * 0
print('-' * 25)
print(f'영유아\t: {group1}명\t: {group1Price}원')
print(f'어린이\t: {group2}명\t: {group2Price}원')
print(f'청소년\t: {group3}명\t: {group3Price}원')
print(f'성인\t\t: {group4}명\t: {group4Price}원')
print(f'어르신\t: {group5}명\t: {group5Price}원')
sum = group1Price + group2Price + group3Price + group4Price + group5Price
sumFormat = format(sum, ',')
print('-' * 25)
print(f'1일 요금 총합계: {sumFormat}원')
print('-' * 25)-------------------------
영유아 : 5명 : 0원
어린이 : 6명 : 1200원
청소년 : 4명 : 1200원
성인 : 47명 : 23500원
어르신 : 38명 : 0원
-------------------------
1일 요금 총합계: 25,900원
-------------------------
친구 이름 다섯 명을 리스트에 저장하고 오름차순과 내림차순으로 정렬해보자.
friends = []
for i in range(5):
friends.append(input('친구 이름 입력: '))
print(f'친구들 : {friends}')
friends.sort()
print(f'오름차순 : {friends}')
friends.sort(reverse=True)
print(f'내림차순 : {friends}')
친구 이름 입력: 김지은
친구 이름 입력: 김은지
친구 이름 입력: 김보람
친구 이름 입력: 김성훈
친구 이름 입력: 김람보
친구들 : ['김지은', '김은지', '김보람', '김성훈', '김람보']
오름차순 : ['김람보', '김보람', '김성훈', '김은지', '김지은']
내림차순 : ['김지은', '김은지', '김성훈', '김보람', '김람보']
다음 리스트에서 중복 아이템(숫자)을 제거하는 프로그램을 만들어보자
numbers = [2, 22, 7, 8, 9, 2, 7, 3, 5, 2, 7, 1, 3]
print(f'numbers : {numbers}')
for n in numbers:
if numbers.count(n) >= 2:
numbers.remove(n)
print(f'numbers : {numbers}')numbers : [2, 22, 7, 8, 9, 2, 7, 3, 5, 2, 7, 1, 3]
numbers : [22, 8, 9, 5, 2, 7, 1, 3]
4개의 숫자 중 서로 다른 숫자 2개를 선택해서 만들 수 있는 모든 경우의 수를 출력하는 프로그램을 만들어보자
numbers = [4, 6, 7, 9]
result = []
for n1 in numbers:
for n2 in numbers:
if n1 == n2:
continue
result.append([n1, n2])
print(f'result: {result}')
print(f'result length: {len(result)}')result: [[4, 6], [4, 7], [4, 9], [6, 4], [6, 7], [6, 9], [7, 4], [7, 6], [7, 9], [9, 4], [9, 6], [9, 7]]
result length: 12
4개의 숫자 중 서로 다른 숫자 3개를 선택해서 만들 수 있는 모든 경우의 수를 출력하는 프로그램을 만들어보자
import math
numbers = [4, 6, 7, 9]
result = []
permutation = math.factorial(len(numbers)) / math.factorial((len(numbers) - 2))
print(f'permutation : {int(permutation)}')
for n1 in numbers:
for n2 in numbers:
if n1 == n2:
continue
for n3 in numbers:
if n1 == n3 or n2 == n3:
continue
result.append([n1, n2, n3])
print(f'result: {result}')
print(f'result length: {len(result)}')
import math
permutation = math.factorial(len(numbers)) / math.factorial((len(numbers) - 3))
print(f'permutation : {int(permutation)}')permutation : 12
result: [[4, 6, 7], [4, 6, 9], [4, 7, 6], [4, 7, 9], [4, 9, 6], [4, 9, 7], [6, 4, 7], [6, 4, 9], [6, 7, 4], [6, 7, 9], [6, 9, 4], [6, 9, 7], [7, 4, 6], [7, 4, 9], [7, 6, 4], [7, 6, 9], [7, 9, 4], [7, 9, 6], [9, 4, 6], [9, 4, 7], [9, 6, 4], [9, 6, 7], [9, 7, 4], [9, 7, 6]]
result length: 24
permutation : 24
'프로그래밍 언어 > Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 딕셔너리를 이용한 프로그래밍(파이썬) (0) | 2023.01.24 |
|---|---|
| 튜플을 이용한 프로그래밍(파이썬) (0) | 2023.01.24 |
| in, len(), clear() 딕셔너리(파이썬) (0) | 2023.01.23 |
| del, pop() 딕셔너리 삭제(파이썬) (0) | 2023.01.23 |
| keys()와 values() (파이썬) (0) | 2023.01.23 |
Comments

